- ...
references.1.1
- See also [Chamberlain, 1995, Appendix
VIII], regarding historical
references.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... changes''1.2
- Free translation by the
author, see the quote at the beginning of Chapter 3
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
network1.3
- http://www.geo.fmi.fi/MIRACLE/
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
Polar/VIS1.4
- http://eiger.physics.uiowa.edu/~vis/
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... Lux3.1
- According to Holst [1998, p.
28]
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
taper3.2
- In this text, the term ``ICCD'' is used for the
combination of an image intensifier and a CCD, regardless of
coupling type, or if they are manufactured as one unit or not.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... photoelectrons3.3
- A more detailed
discussion of this noise source is found in works by Holst [1998, pp.
195-200], Trondsen [1998, p. 48],
Csorba [1985, pp. 120-124] and Hertel [1989].
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... unit3.4
- Note the
cables are only about 1 m and flat on the prototype unit
(ccdcam1)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... equation3.5
- from the filter
manufacturer
(http://www.barrassociates.com/terms.php?type=angle), see also
[Jones, 1974]
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... )4.1
- ftp://adc.gsfc.nasa.gov/pub/adc/archives/catalogs/5/5050
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... exercise6.1
- The problem is not so much the
visualisation itself, but rather that human perception has
evolved to interpret 2-D surfaces of 3-D objects. Evolution has
never required an understanding of a true 3-D distribution.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
radiology6.2
- Incidentally, the term ``tomography'' existed in
radiological applications decades before computerised tomography
became a real possibility. See, for example,
Lodin [1935]; Weinbren [1946], and other references
discussed in Backlund [1956]. Typically a series of
X-ray exposures were obtained while the X-ray tube and film-cassette
rotated around the patient. Back then, the tomographic inversion had
to be performed by the brain of the radiologist observing these series
of X-ray images.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... airglow\xspace6.3
- As long as the enhancements were only observed in
the
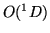 (6300 Ã
) and occasionally in the
(6300 Ã
) and occasionally in the 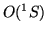 (5577 Ã
) emission
lines, the natural term was ``HF pump-enhanced airglow''. With the recent observations
in the
(5577 Ã
) emission
lines, the natural term was ``HF pump-enhanced airglow''. With the recent observations
in the 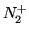 1Pos. (6600 Ã
) emission [Djuth et al., 1999], and
1Pos. (6600 Ã
) emission [Djuth et al., 1999], and 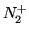 1Neg.
(4278 Ã
) and
1Neg.
(4278 Ã
) and 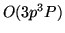 (8446 Ã
), a more correct term would be something
like ``HF pump-enhanced optical emissions'' or maybe ``Radio-induced
optical emissions''. However, the old term ``HF pump-enhanced airglow'' will be
retained in this text for compatibility with earlier papers.
(8446 Ã
), a more correct term would be something
like ``HF pump-enhanced optical emissions'' or maybe ``Radio-induced
optical emissions''. However, the old term ``HF pump-enhanced airglow'' will be
retained in this text for compatibility with earlier papers.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... tenA.1
- Two additional structures have been built for other
users
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.