 |



Next: Transmission of the optics
Up: The Forward model -
Previous: Atmospheric absorption
Contents
Effective collecting area
The effective collecting area is, in the simplest approximation, the
area of the front lens as seen from the voxel. The variation of the
effective area with angle 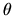 relative to the optical axis
is: relative to the optical axis
is:
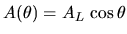 |
(5.16) |
Here 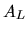 is the maximum area of the front lens or the
aperture of the optics and is the maximum area of the front lens or the
aperture of the optics and 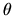 is the angle relative to the
optical axis. This formula is good enough for single thin lens
optics. For more complex optical systems with a large number of lenses
and apertures, the effects of mechanical vignetting -- the decrease
of effective aperture with increasing angle relative to the optical
axis -- must be corrected for. The higher order corrections that are
needed must be determined from measurements. This can be accomplished
with a simple experiment in which a narrow weak beam of parallel light
illuminates the front lens at varying angles relative to
the optical axis and with varying translation from the centre of the front
lens. This has yet to be done for the ALIS cameras. is the angle relative to the
optical axis. This formula is good enough for single thin lens
optics. For more complex optical systems with a large number of lenses
and apertures, the effects of mechanical vignetting -- the decrease
of effective aperture with increasing angle relative to the optical
axis -- must be corrected for. The higher order corrections that are
needed must be determined from measurements. This can be accomplished
with a simple experiment in which a narrow weak beam of parallel light
illuminates the front lens at varying angles relative to
the optical axis and with varying translation from the centre of the front
lens. This has yet to be done for the ALIS cameras.



Next: Transmission of the optics
Up: The Forward model -
Previous: Atmospheric absorption
Contents
copyright Björn Gustavsson 2000-10-24
|

![]() relative to the optical axis
is:
relative to the optical axis
is: